
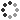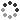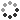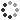
Illustration of the action of pesticides on human cells, increasing the risk of non-Hodgkin抯 lymphoma, Parkinson抯 disease and prostate cancer. The first action of pesticides on B-lymphocytes is genotoxic, pesticides reach cellular DNA and cause the displacement of the Bcl2 gene (yellow) of chromosome 18 towards chromosome 14, causing an anarchic proliferation of B-lymphocytes. The second action affects NK-lymphocytes, which are specialized in eliminating abnormal cells such as mutated B-lymphocytes. Pesticides disrupt the production of molecules that usually allow abnormal cells to be eliminated; mutated B-lymphocytes proliferate anarchically as they are no longer eliminated by NK-lymphocytes.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP19632652
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
No
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading