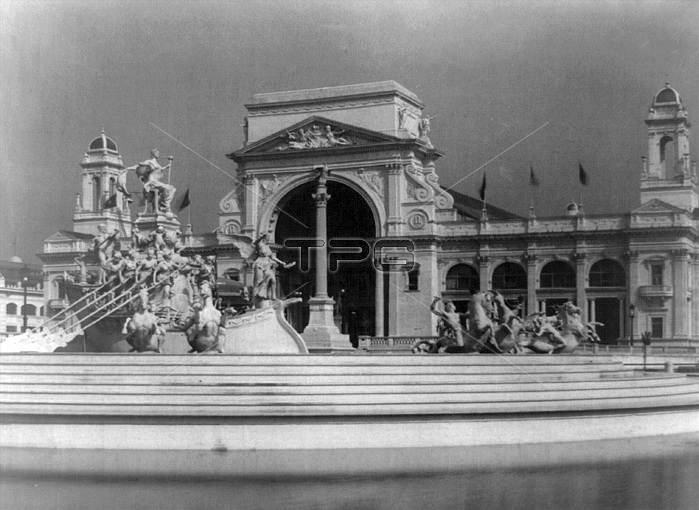
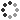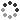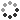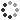
The World's Columbian Exposition was a world's fair held in Chicago in 1893 to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus' arrival in the New World in 1492. Most of the buildings of the fair were designed in the neoclassical architecture style. The area at the Court of Honor was known as The White City. Facades were made not of stone, but of a mixture of plaster, cement, and jute fiber called staff, which was painted white, giving the buildings their "gleam". Architecture critics derided the structures as "decorated sheds". The buildings were clad in white stucco, which, in comparison to the tenements of Chicago, seemed illuminated. It was also called the White City because of the extensive use of street lights, which made the boulevards and buildings usable at night. Frederick William MacMonnies (September 28, 1863 - March 22, 1937) was an expatriate American sculptor of the Beaux-Arts school. In 1891 he was awarded the commission for the Columbian Fountain, the centerpiece of the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago: the sculpture of Columbia in her Grand Barge of State, in the vast central fountain of the Court of Honor, was truly the iconic figure at the heart of the American Beaux-Arts movement. Photographed by the Allgeier Company, 1893.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP22174059
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
No
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading