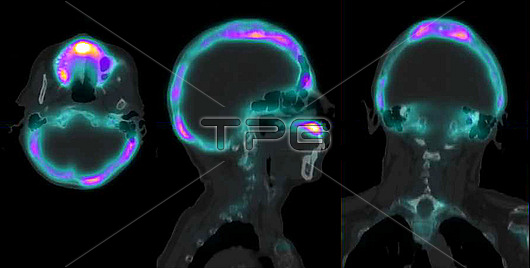
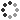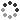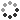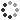
Composite computed tomography-single-photon emission computed tomography (CT-SPECT) scans of an axial (left), sagittal (centre) and coronal (right) section of the skull of a 70 year old woman with Pagets disease of bone, revealing thickening of the skull. Pagets disease disrupts the normal cycle of bone renewal, leading to weakened and potentially deformed bones. Here, increased radiotracer uptake (colourful) can be seen in the skull due to abnormal and excessive remodelling of the bone. The radioactive tracer is technetium (Tc-99m). The condition typically affects only one or a few bones, most commonly the pelvis, skull, spine, and femur. While many individuals with Pagets disease do not experience symptoms, the changes in bone structure can lead to pain, misshapen bones, and fractures. This condition is rare in individuals under 40 years of age. The exact cause of Pagets disease is unknown, although both environmental and genetic factors are believed to contribute. While there is no cure for the disease, treatments such as bisphosphonates, physiotherapy, and surgery can help alleviate symptoms.
| px | px | dpi | = | cm | x | cm | = | MB |
Details
Creative#:
TOP30231552
Source:
達志影像
Authorization Type:
RM
Release Information:
須由TPG 完整授權
Model Release:
N/A
Property Release:
N/A
Right to Privacy:
No
Same folder images:
 Loading
Loading